ACL
Role required: security_admin.
Use ACL (Access Control List) to specify the users and/or processes allowed to access the objects, and operations allowed on the given objects.
In SimpleOne, rules for ACLs check users against a set of requirements before they are allowed to work with the data.
ACL rules specify:
- The object to secure.
- The operation to secure.
- The required permissions.
Objects
ACL restricts access to the object. Each object consists of the type and the name of a table, field, or record.
The following table gives examples of objects:
| Type | Table | Column | Object Secured |
|---|---|---|---|
| record | Problem (itsm_problem) | (not set) | The Problem table. |
| record | Incident (itsm_incident) | Active | The Active field in the Incident table. |
Operations
In ACL, the term operation refers to a valid action carried out on the specified object. Multiple operations can be carried out on some objects, like records.
This table gives examples of operations:
| Type | Table | Column | Object Secured |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Create] | itsm_problem | (not set) | Creating records in the Problem table. Generated ACL record name is [Create].itsm_problem |
| [Write] | itsm_incident | active | Updating the Active field in the Incident table. Generated ACL record name is [Write].itsm_incident.active |
Permissions
The permissions specify the details of the access to the named object and operation. Responsible persons should specify permission with the following information:
- User roles in the Role field.
- Conditions.
- The script returning true or false or setting the answer variable to true or false.
See the Create ACL Rules article to learn more.
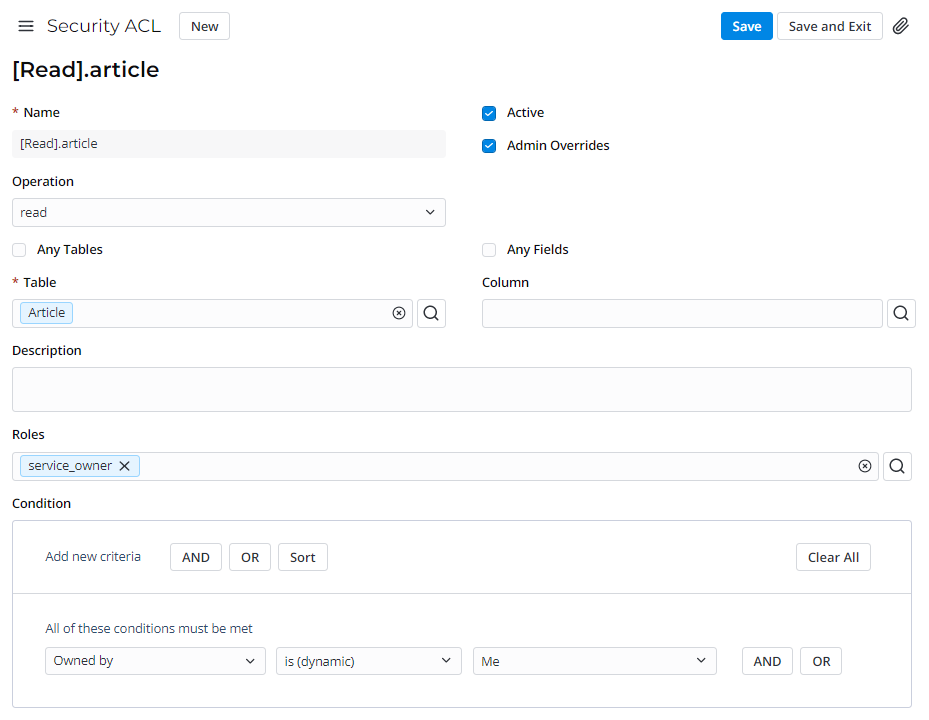
To perform a particular operation over a particular object, a user must pass ALL permissions listed in the access control rule. For example, to access an active record in the Article table, a user must meet the following conditions:
| Permission type | Requirement | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Roles | Required role: service_owner | Only users with the service_owner role can read articles. |
| Condition | Owned by is (dynamic) Me | The article is available to the owner of the Content Item this article is related to. An empty condition always returns true. |
The acl.disabled property allows you to disable all ACL checks.
To disable security checks, follow the steps below:
- Navigate to System Properties → ACL Property.
- In the Value field, enter true to disable security ACL or false to enable it.
- Click Save or Save and exit.
If you enable this property, it may result in unauthorized access to your SimpleOne instance data. So use it carefully and do not forget to turn it off after all necessary operations.
How ACL evaluate permissions
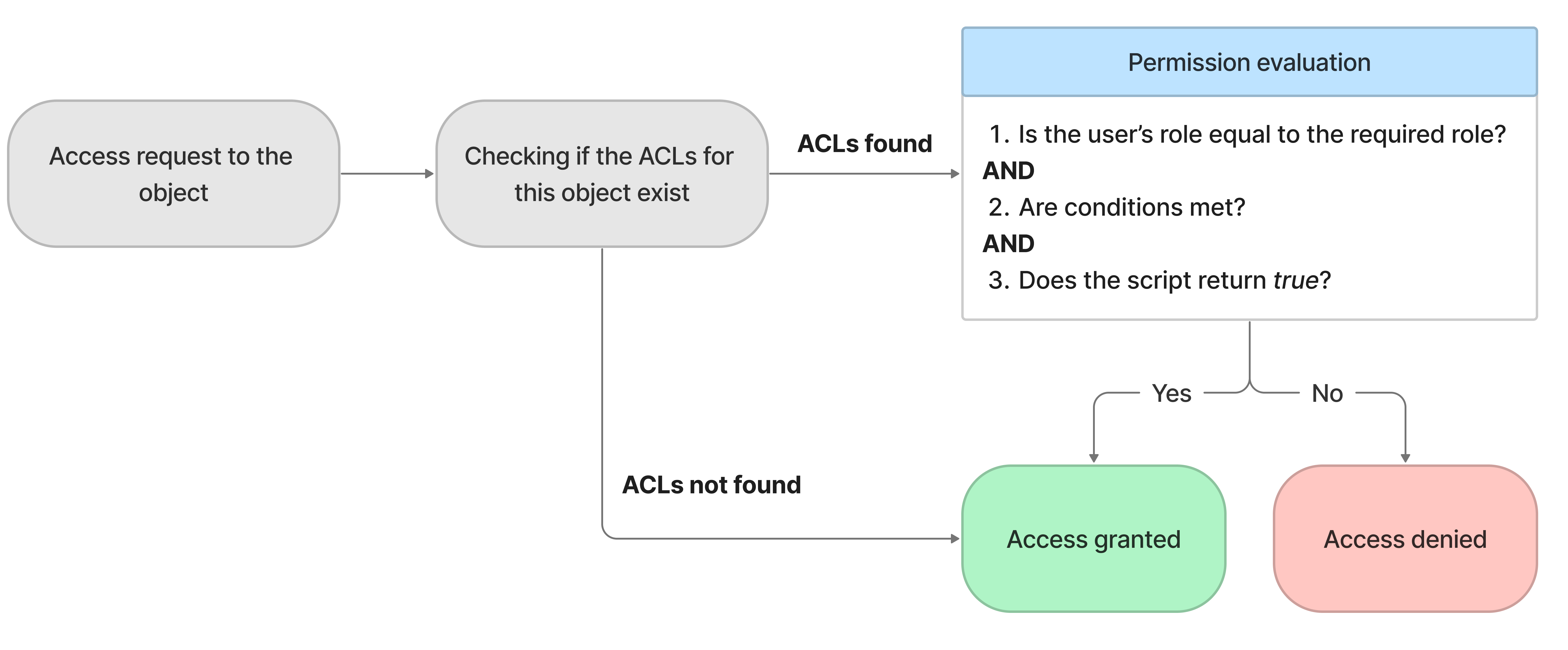
- When the data is requested, the system checks if there are ACL rules related to the requested object and operation.
- If there is a rule, the system checks the user against all the requirements and then either permits access to the object and operation or denies it.
- If the user does not meet one of the requirements, the system restricts access.
- The system checks all rules related to the requested object. If the user does not meet all ACL's requirements for the requested object and operation, the system denies access to them.
If the requested object and operation do not have related ACLs, the user gets access to it. However, it is a rare case: a set of default access control rules protecting all record operations are delivered in “out-of-the-box” configuration.
The access denial affects on what the user can see or do, depending on the ACL rule itself. For example, if a read ACL is denied, the system restricts the user to view the object. Depending on the object, the user does not see fields, records from a list, or UI pages.
The table below lists the results of failing an ACL rule for a particular operation and object type.
| Operation | Results of ACL rule failing |
|---|---|
| Create | The New user interface action is not displayed on pages for the user. Users cannot also insert records into tables via API protocols. If there is a condition in the create ACL that specifies a field value, it always returns false. In newly created records, fields are regarded as empty until the record is saved. |
| Read | The form and list objects are not displayed for the user. Users cannot also retrieve records via API protocols. |
| Write | The form fields are not editable for the user: they are read-only. Users cannot also update records via API protocols. |
| Delete | The Delete user interface action is not displayed on pages for the user. Users cannot also insert records into tables via API protocols. |